Windows startup errors can be frustrating, but troubleshooting and resolving them quickly is possible with a systematic approach. Startup errors are often caused by hardware failures, corrupted system files, or software conflicts. The first step in troubleshooting is identifying the nature of the error. Typically, error messages are displayed on the screen during startup, providing valuable information about the problem. If no message appears, the system may be stuck in a boot loop or displaying a blank screen, which indicates a more serious issue. Begin by performing a safe boot. This can be done by pressing the F8 key or Shift + F8 on newer systems during startup to access the Advanced Boot Options menu. Safe Mode loads only essential drivers and services, which can help bypass problematic software or driver conflicts. Once in Safe Mode, you can run a system scan using the System File Checker SFC command to detect and repair corrupted system files.
Open the command prompt and type easy pc fix, and then press Enter. This process may take some time but can resolve many system file-related startup issues. If Safe Mode does not work, try Startup Repair, a built-in Windows tool designed to fix boot issues automatically. Access it through the Windows Recovery Environment WinRE by restarting the computer and pressing the F11 or Esc key depending on the manufacturer. Once in WinRE, navigate to Troubleshoot, then Advanced Options, and select Startup Repair. The tool will scan your system for issues and attempt to fix them without affecting personal data. Another common culprit of startup errors is recent software or driver installations. If you suspect a recent update or installation is causing the problem, use System Restore to roll back your system to a previous state when it was functioning properly.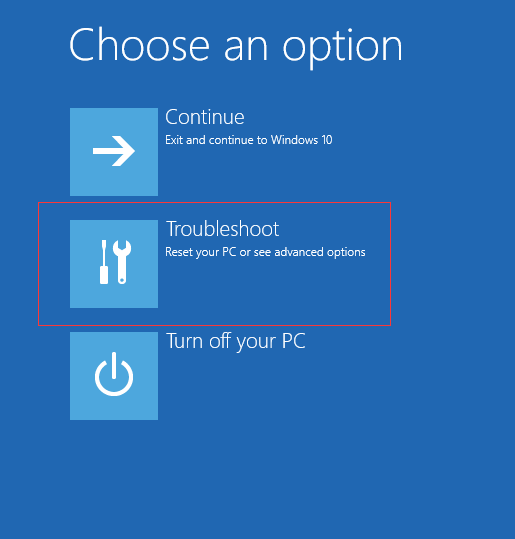
You can access this through WinRE by selecting System Restore under the Advanced Options menu. For hardware-related errors, such as a failing hard drive or RAM issues, check the system’s BIOS or UEFI settings. Restart your computer and press the designated key often F2, Delete, or Esc to enter the BIOS setup. Here, ensure that the boot drive is correctly recognized and configured. Running hardware diagnostics can also help identify failing components that may be preventing the system from starting. Lastly, if none of these solutions work, you may need to perform a clean installation of Windows. This should be a last resort, as it will remove all data on the system. Back up your files regularly to avoid data loss in case of such a situation. By following these steps, you can efficiently diagnose and resolve most Windows startup errors and get your system running again.
