Industrial pneumatic systems utilize compressed air to transmit and control energy, playing a crucial role in a variety of manufacturing processes. Understanding the key components of these systems is essential for optimizing their performance and ensuring efficient operation. The primary components include compressors, storage tanks, filters, regulators, valves, actuators, and tubing. At the heart of any pneumatic system is the compressor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy by compressing atmospheric air. Compressors come in various types, including reciprocating, rotary screw, and centrifugal compressors, each offering distinct advantages depending on the application. The compressed air produced by these machines is then stored in storage tanks or receivers. These tanks not only hold air until it is needed but also help to smooth out pressure fluctuations that can occur during system operation. Once the air is stored, it must be processed to ensure quality and consistency. This is where filters come into play. Air filters remove moisture, dust, and other contaminants from the compressed air before it reaches downstream components.
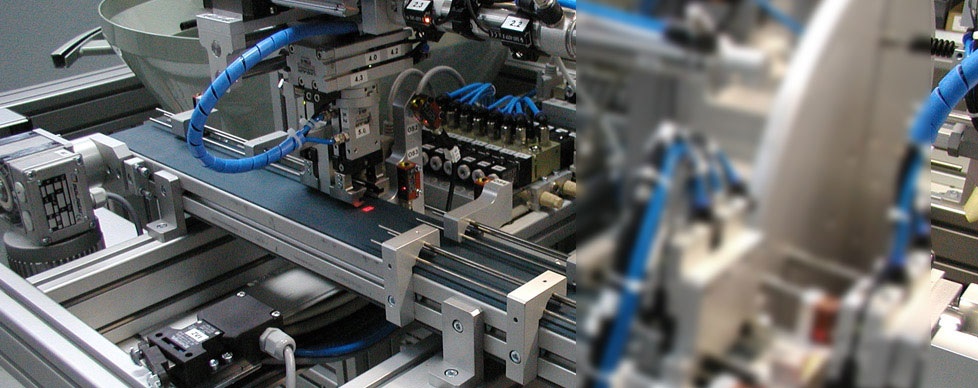
Contaminants can damage sensitive equipment and affect the quality of processes that rely on pneumatic power. Alongside filters, regulators are vital for controlling the pressure of the compressed air as it flows through the system. Regulators ensure that air is delivered at the correct pressure, which is critical for maintaining optimal performance of pneumatic tools and actuators. Valves are essential for controlling the flow and direction of compressed air within the system. There are several types of valves, including directional control valves, flow control valves, and shut-off valves. Directional control valves manage the path that air takes, allowing for the activation and deactivation of specific actuators. Flow control valves adjust the speed of air flow, enabling precise control over the operation of pneumatic devices and see this pneumatig.eu. Shut-off valves provide the ability to isolate sections of the system for maintenance or troubleshooting. Actuators, which include cylinders and rotary actuators, are responsible for converting the energy from compressed air into mechanical motion.
Pneumatic cylinders are commonly used to create linear motion, while rotary actuators provide rotational movement. These devices are essential for driving various industrial applications, from conveyor systems to robotic arms. The performance of actuators is directly influenced by the quality and pressure of the compressed air they receive, making the proper functioning of all upstream components crucial. Tubing and fittings form the network through which compressed air travels. The choice of materials and dimensions for the tubing is important for minimizing pressure drops and ensuring efficient air delivery. Common materials for pneumatics distributor tubing include nylon, polyurethane, and metal, each suited for specific applications. Proper installation and maintenance of tubing and fittings are also critical, as leaks can lead to significant losses in system efficiency and increased operational costs. In conclusion, the efficiency and effectiveness of industrial pneumatic systems depend heavily on the careful selection and maintenance of their key components. Compressors, storage tanks, filters, regulators, valves, actuators, and tubing each play a vital role in the overall functionality of these systems.
